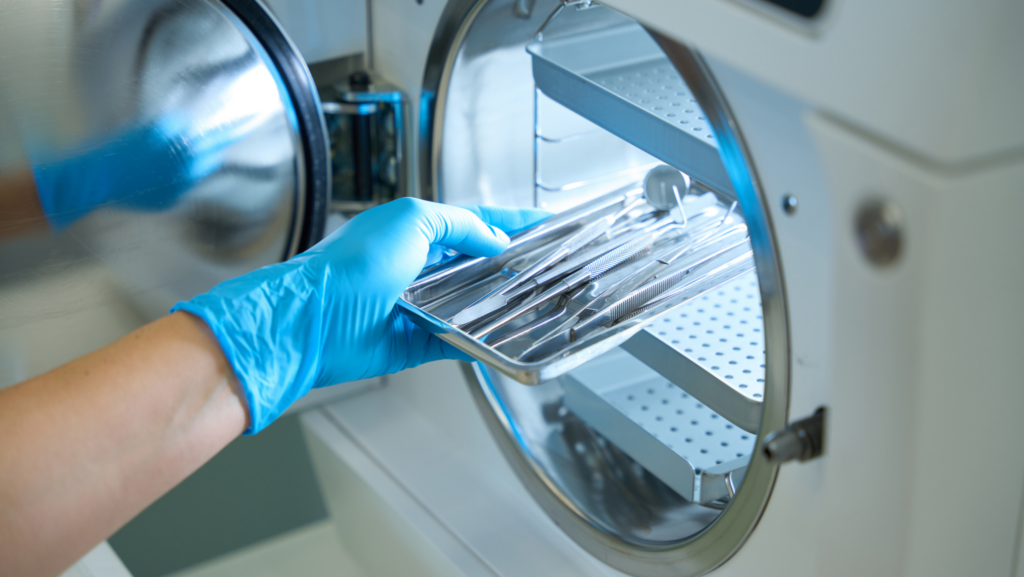
The cornerstone of patient safety in dental practice lies in proper instrument sterilization and meticulous documentation. As the Royal College of Dental Surgeons of Ontario (RCDSO) continues to emphasize stringent sterilization protocols, dental practices face increasing challenges in maintaining comprehensive records while managing busy clinical schedules.
Critical parameters in instrument sterilization
The RCDSO guidelines mandate specific parameters for instrument reprocessing that must be monitored and documented:
1. Physical parameters
– Time
– Temperature
– Pressure
– Proper packaging
– Load configuration
2. Chemical indicators
– External indicators on each package
– Internal chemical indicators
– Integration of Class 5 or 6 indicators
3. Biological monitoring
– Daily spore testing
– Documentation of results
– Follow-up procedures for failed tests
Documentation requirements
The RCDSO requires maintaining detailed records of:
– Sterilization cycle parameters
– Load contents and identification
– Operator responsible for the load
– Results of all monitoring processes
– Equipment maintenance and validation testing
– Any failed cycles and corrective actions taken
The digital evolution of sterilization documentation
Traditional paper-based logging systems present several challenges:
– Time-consuming manual entry
– Potential for human error
– Storage and retrieval difficulties
– Inconsistent documentation practices
– Limited accessibility for audits
Modern digital solutions address these challenges through:
– Automated parameter recording
– Real-time monitoring capabilities
– Secure cloud-based storage
– Immediate access to historical data
– Standardized documentation protocols
Risk management through digital innovation
Digital sterilization tracking systems provide enhanced risk management through:
1. Automated compliance
– Pre-programmed parameter verification
– Immediate alert systems for deviations
– Standardized documentation formats
2. Enhanced traceability
– Instrument-specific tracking
– Patient-procedure correlation
– Complete cycle history accessibility
3. Quality assurance
– Automated maintenance schedules
– Integration of biological monitoring results
– Real-time process verification
Implementation considerations
When transitioning to digital sterilization documentation, practices should consider:
1. Staff training requirements
2. Integration with existing workflows
3. Data backup and security measures
4. Accessibility across multiple devices
5. Compliance with privacy regulations
Conclusion
As dental practices evolve, digital solutions for sterilization documentation become increasingly essential for maintaining compliance and ensuring patient safety. The integration of technology in sterilization monitoring not only enhances compliance with RCDSO guidelines but also improves practice efficiency and risk management.
(Disclaimer: The author discloses a financial interest in SteriCentre (www.SteriCentre.com), a digital platform for dental instrument sterilization tracking and documentation available through the App Store.)
References:
1. Royal College of Dental Surgeons of Ontario. “Guidelines for Infection Prevention and Control in Dental Practice.” 2025
2. Centres for Disease Control and Prevention. “Guidelines for Infection Control in Dental Health-Care Settings.” 2024
3. Canadian Standards Association. “Sterilization of Health Care Products.” CAN/CSA Z314-18, 2024
4. Ontario Dental Association. “Best Practices for Infection Prevention and Control.”2023
About the author:
Dr. Joel Eisenstat practiced dentistry for 35 years before retiring from clinical practice. He now focuses on developing technological solutions for dental infection control and sterilization management through SteriCentre, a digital platform for instrument sterilization tracking and documentation.